About: Relay lens Goto Sponge NotDistinct Permalink
An Entity of Type : yago:Whole100003553,
within Data Space : dbpedia.org associated with source document(s)

![http://dbpedia.org/describe/?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdbpedia.org%2Fresource%2FRelay_lens&graph=http%3A%2F%2Fdbpedia.org&graph=http%3A%2F%2Fdbpedia.org]()

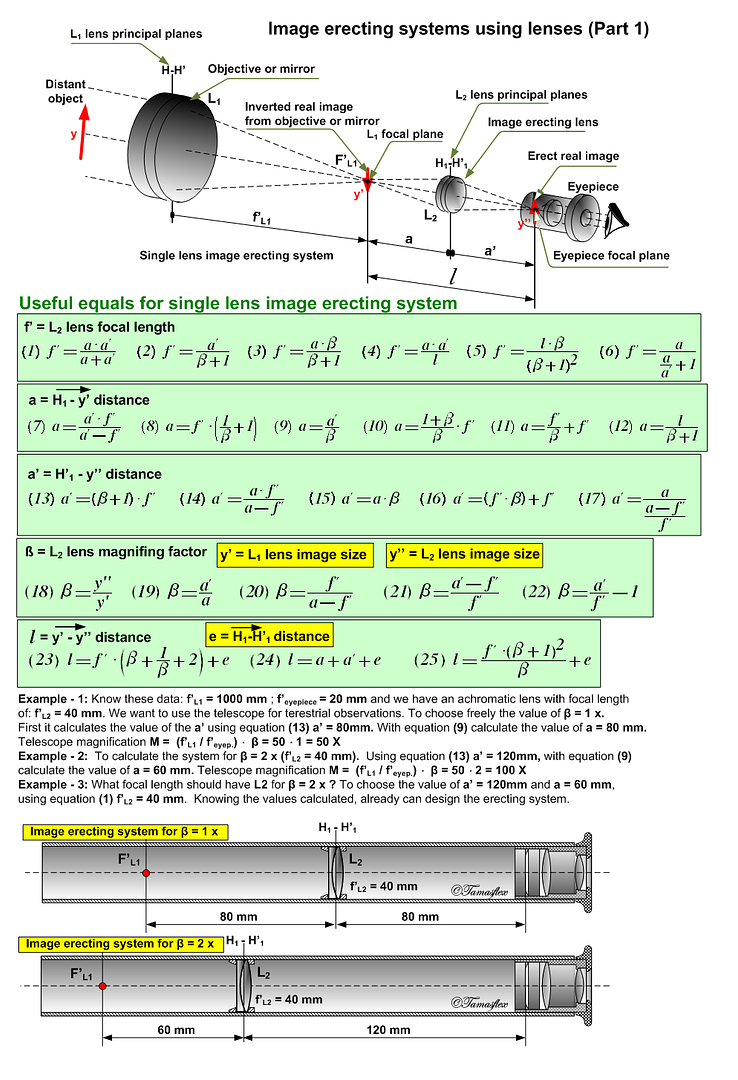
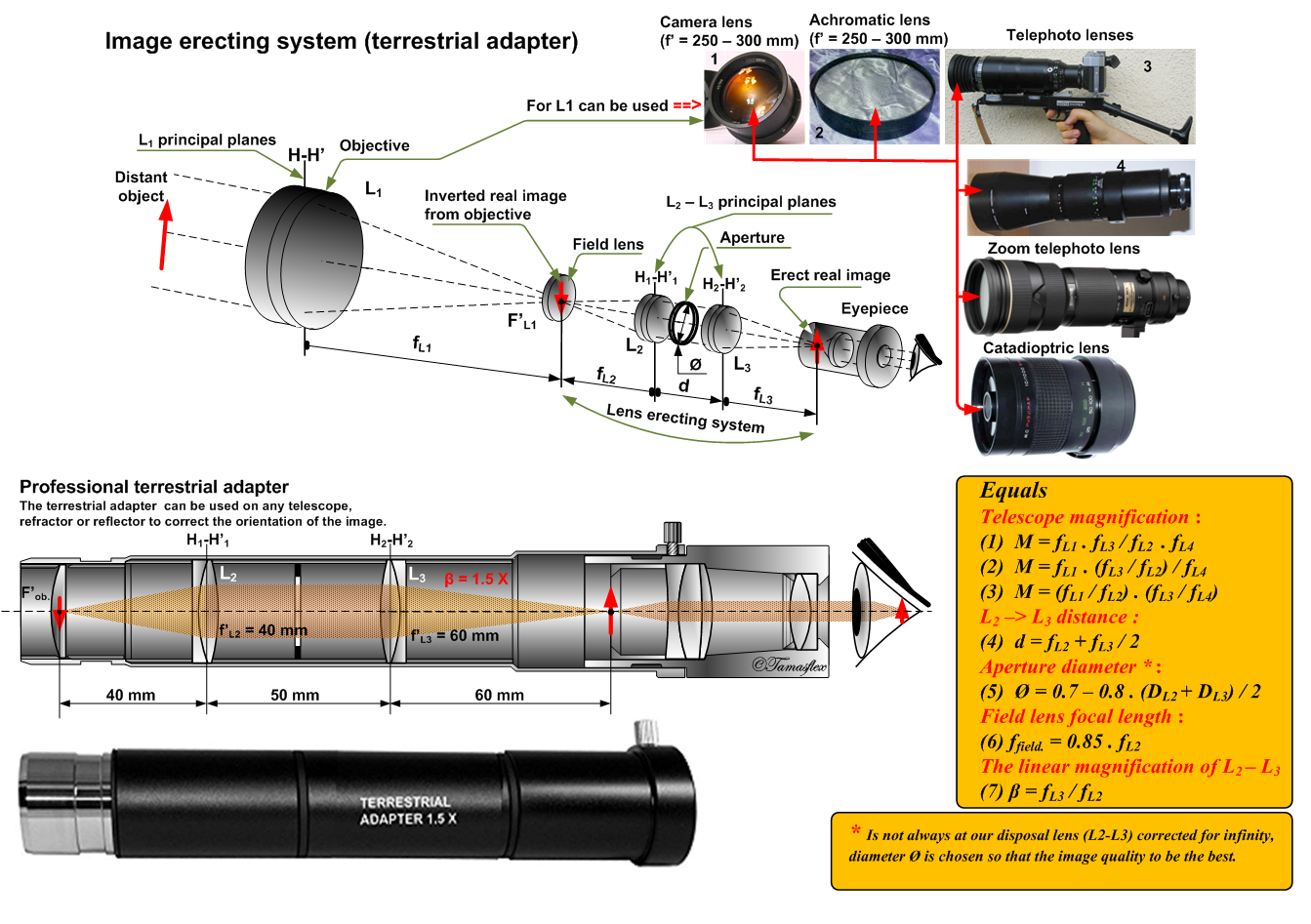
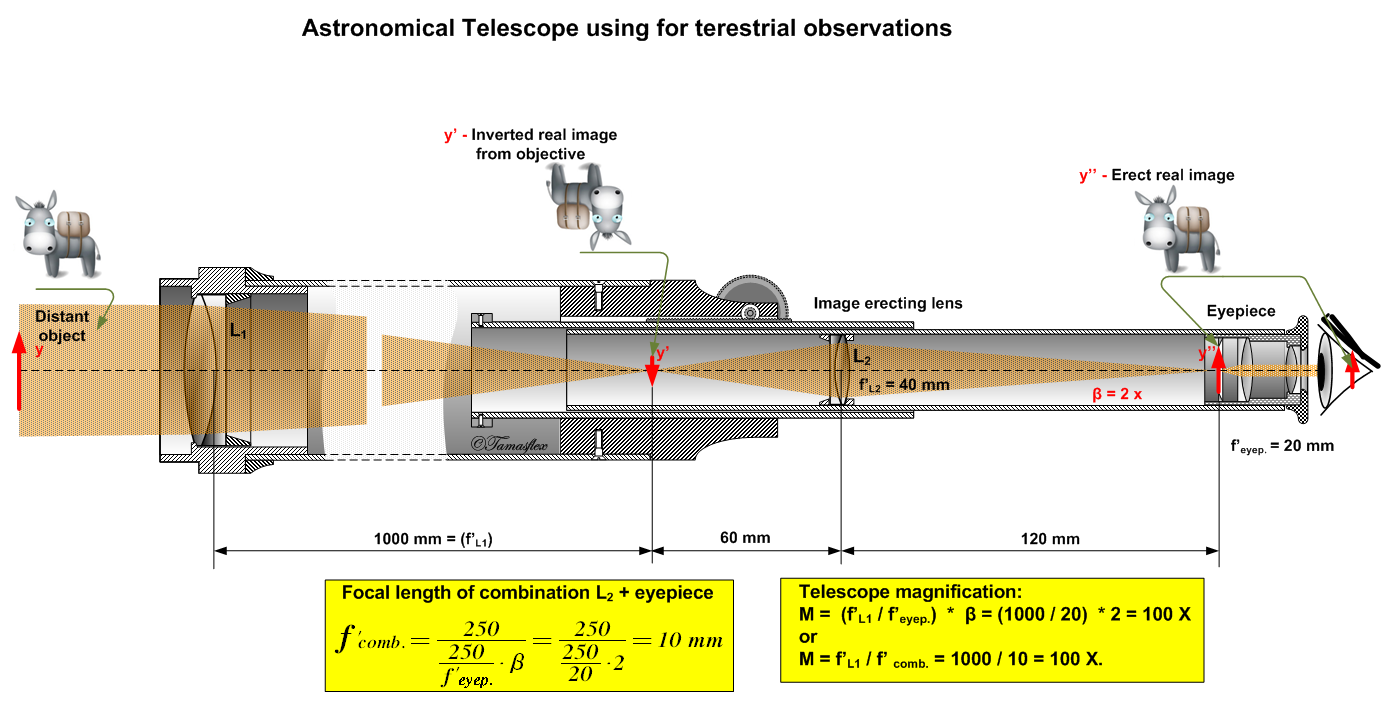
In optics, a relay lens is a lens or a group of lenses that receives the image from the objective lens and relays it to the eyepiece. Relay lenses are found in refracting telescopes, endoscopes, and periscopes to optically manipulate the light path, extend the length of the whole optical system, and usually serve the purpose of inverting the image. They may be made of one or more conventional lenses or achromatic doublets, or a long cylindrical gradient-index of refraction lens (a GRIN lens).
| Attributes | Values |
|---|---|
| rdf:type | |
| rdfs:label |
|
| rdfs:comment |
|
| foaf:depiction | |
| dcterms:subject | |
| Wikipage page ID |
|
| Wikipage revision ID |
|
| Link from a Wikipage to another Wikipage |
|
| Link from a Wikipage to an external page | |
| sameAs | |
| dbp:wikiPageUsesTemplate | |
| thumbnail | |
| has abstract |
|
| prov:wasDerivedFrom | |
| page length (characters) of wiki page |
|
| foaf:isPrimaryTopicOf | |
| is Link from a Wikipage to another Wikipage of | |
| is Wikipage redirect of | |
| is foaf:primaryTopic of |
Faceted Search & Find service v1.17_git139 as of Feb 29 2024


![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)

OpenLink Virtuoso version 08.03.3330 as of Mar 19 2024, on Linux (x86_64-generic-linux-glibc212), Single-Server Edition (378 GB total memory, 50 GB memory in use)
Data on this page belongs to its respective rights holders.
Virtuoso Faceted Browser Copyright © 2009-2024 OpenLink Software


![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)
OpenLink Virtuoso version 08.03.3330 as of Mar 19 2024, on Linux (x86_64-generic-linux-glibc212), Single-Server Edition (378 GB total memory, 50 GB memory in use)
Data on this page belongs to its respective rights holders.
Virtuoso Faceted Browser Copyright © 2009-2024 OpenLink Software










![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png)
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png)
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png)